The Thyroid
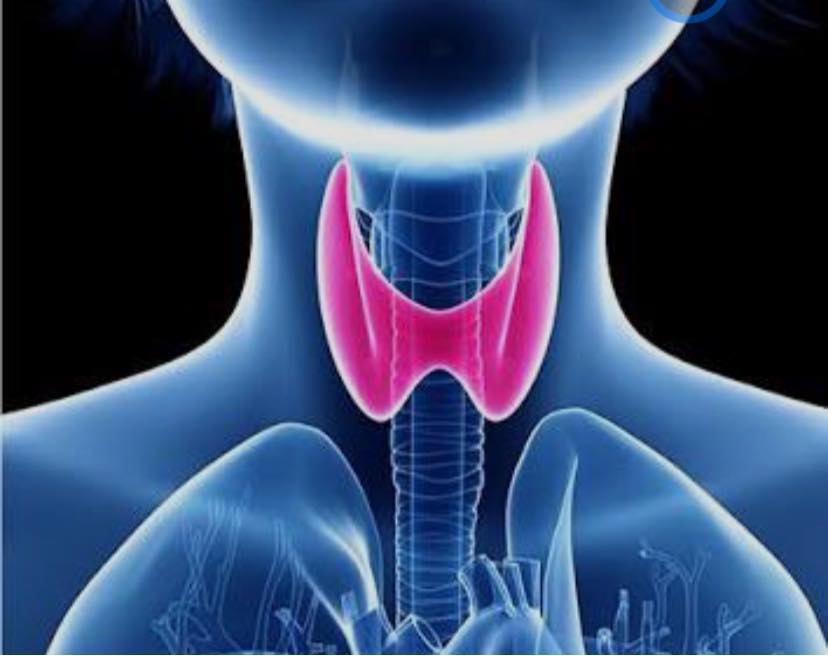
The THYROID is situated just below your “Adams apple” or larynx.
During development (inside the womb) the thyroid gland originates in the back of the tongue, but it normally migrates to the front of the neck before birth.
The function of the thyroid gland is to take iodine, found in many foods, and convert it into thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid cells are the only cells in the body which can absorb iodine. These cells combine iodine and the amino acid tyrosine to make T3 and T4. T3 and T4 are then released into the blood stream and are transported throughout the body where they control metabolism (conversion of oxygen and calories to energy).
Every cell in the body depends upon thyroid hormones for regulation of their metabolism. The normal thyroid gland produces about 80% T4 and about 20% T3, however, T3 possesses about four times the hormone “strength” as T4.
The thyroid regulates. :
- Breathing
- Heart rate
- Central and peripheral nervous systems
- Body weight
- Muscle strength
- Menstrual cycles›
- Body temperature
- Cholesterol levels
Below are other symptoms of too much T3 and T4 in your body (hyperthyroidism):
- Anxiety
- Irritability or moodiness
- Nervousness, hyperactivity
- Sweating or sensitivity to high temperatures
- Hand trembling (shaking)
- Hair loss
- Missed or light menstrual periods
Below are other symptoms that may indicate too little T3 and T4 in your body (hypothyroidism):
- Trouble sleeping
- Tiredness and fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Dry skin and hair
- Depression
- Sensitivity to cold temperature
- Frequent, heavy periods
- Joint and muscle pain
HOW TO DEAL WITH A TIRED THYROID
- Get more rest. If you’re regularly fatigued even though your thyroid treatment is optimised.
- Optimize your sleep. …
- Keep a sleep diary. …
- Change your diet. …
- Get moving. …
- Make time to relax. …
- Stay on top of stress.
Taking certain vitamin supplements can have an effect on your thyroid health.
Low thyroid hormones can affect your body’s vitamin B-12 levels. Taking a vitamin B-12 supplement may help you repair some of the damage hypothyroidism caused.
…
Vitamin B
- peas and beans.
- asparagus.
- sesame seeds.
- tuna.
- cheese.
- milk.
- eggs.
Here are specific nutrients that may be beneficial for hypothyroidism.
- Iodine Is Needed to Make Thyroid Hormone.
- Vitamin B Is Important for Thyroid Function.
- Selenium Is Essential for Thyroid Hormone Metabolism.
- Zinc Helps Synthesize Thyroid Hormone.
- Tyrosine, in Combination With Iodine, Produces Thyroid Hormone.